Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
Tags
- web server
- Spring
- ORM
- spring cloud
- 컨테이너
- 데이터베이스
- 배포
- Spring Security
- computer science
- 웹 서버
- 스프링
- 스프링 부트
- virtualization
- vm
- 영속성 컨텍스트
- HTTP
- CS
- 도커
- Container
- JPA
- 가상화
- 스프링 배치
- 스프링 시큐리티
- spring boot
- mysql
- CI/CD
- spring batch
- Java
- 자바
- 백엔드
Archives
- Today
- Total
개발 일기
[Information Security] Symmetric Encryption and Message Confidentiality 본문
Computer Science/보안
[Information Security] Symmetric Encryption and Message Confidentiality
개발 일기장 주인 2025. 3. 30. 12:38
<Classified along three independent dimensions>
Type of operations
﹒substitution : each element in the plaintext is mapped into another element
﹒transposition : elements in plintext are reagrranged
The number of keys used
﹒symmetric : sender & receiver use same key
﹒asymmetric : sender & receiver each use a different key
The way in which the plaintext is processed
﹒block cipher : processes input one block of elements at a time
﹒stream cipher : processes the input elements continuously
🟠 Symmetric Encryption ( ≒ Conventional Encryption ≒ Single-Key Encryption )
- most widely used alternative because of speed
- Plaintext/Ciphertext/Encryption algorithm/Decryption algorithm/Secret Key
🟠 Computationally Secure Encryption Schemes
- Encryption is computationally secure if:
- Cost of breaking cipher exceeds value of information
- Time required to break cipher exceeds the useful lifetime of the information
- difficult to estimate the amount of effort required to break
- but can estimate time/cost of a brute-force attack
🟠 Fiestel Cipher Structure
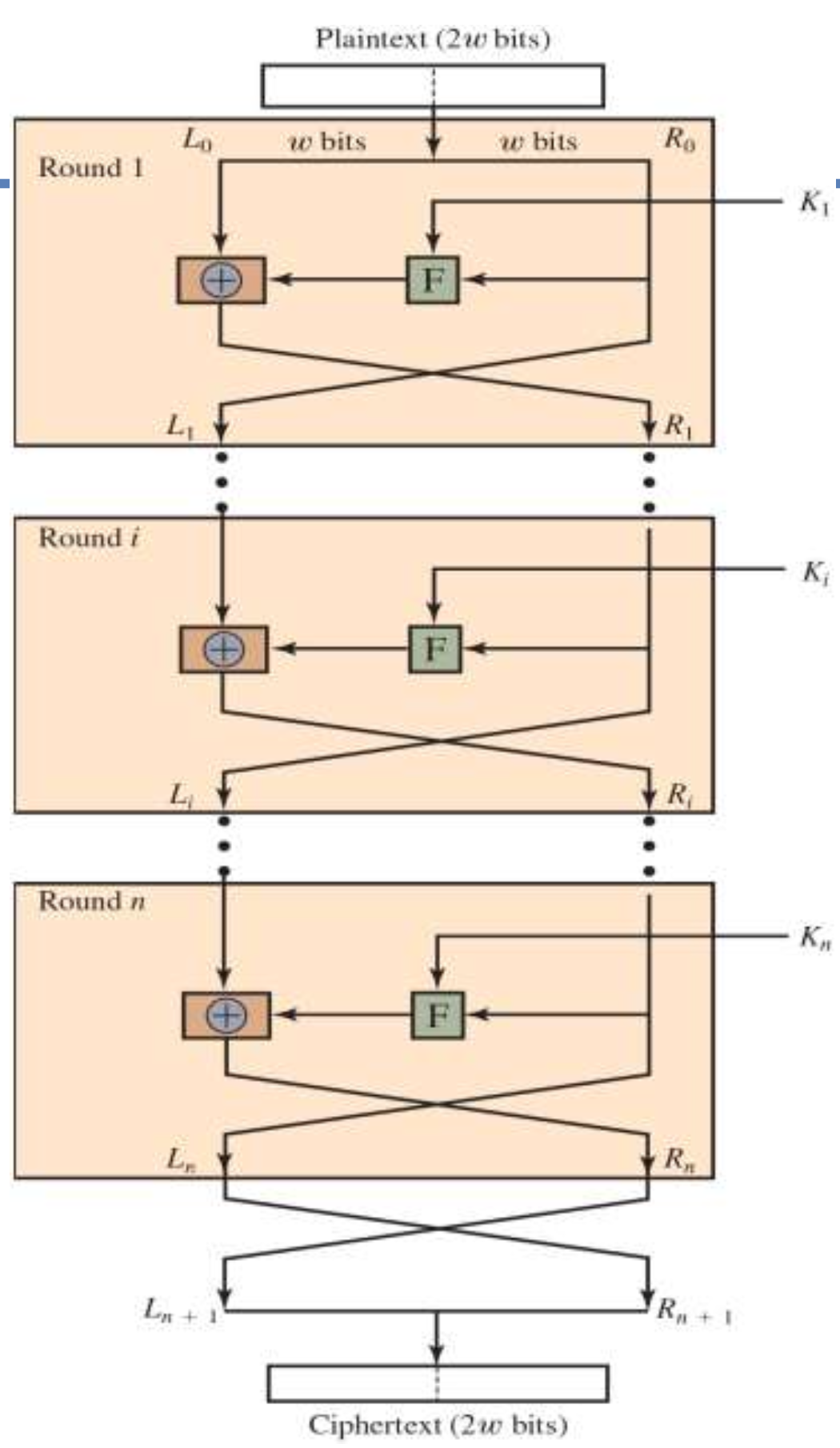
- Block Cipher based such as DES / Triple DES
- strength depends on F
- can easily make the decryption method
(just reverse of this procedure) - Each round uses a round key, which is generated through the key expansion process.
- 평문(P)을 두 개의 w비트 블록으로 나눠서 시작
P = L_0 + R_0 - 여러 라운드(Round) 반복
R_i+1 = L_i ⊕ F(R_i, K_i+1)
L_i+1 = R_i - 최종적으로 L과 R을 병합하여 암호문(Ciphertext) 생성
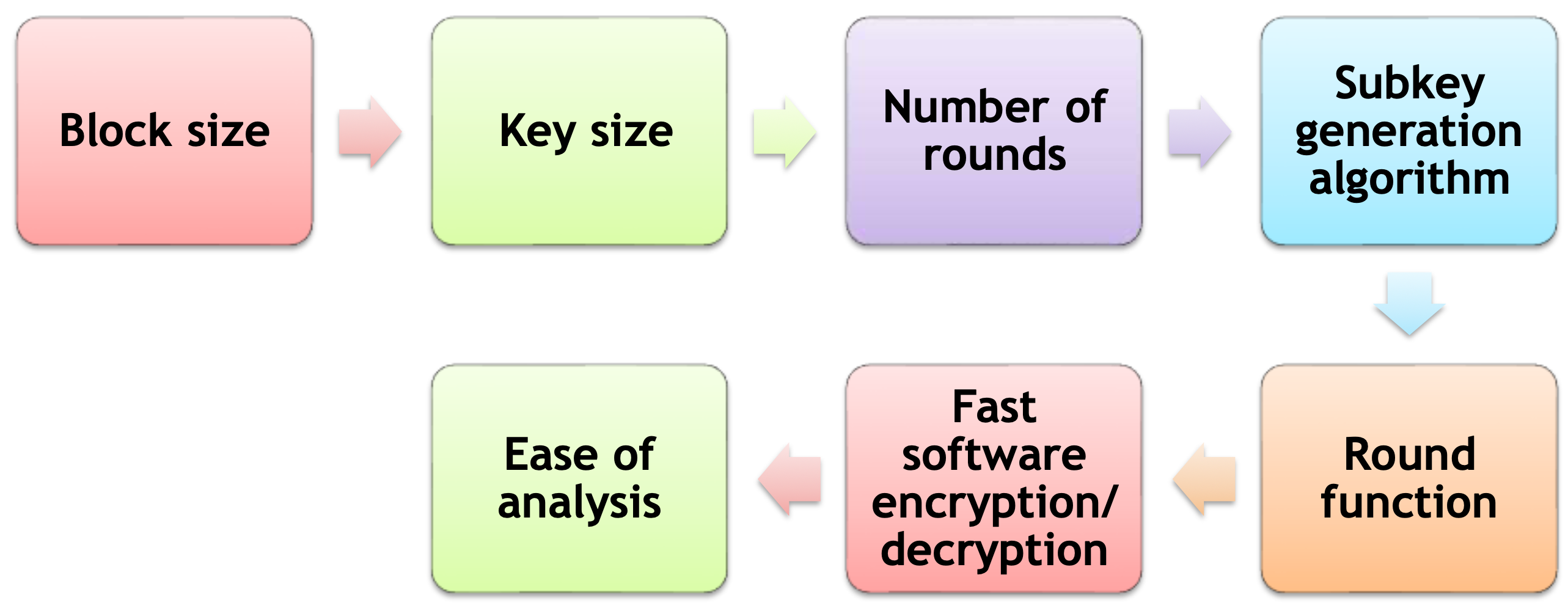
🔸 Block Cipher Structure
Symmetric block cipher consists of :
- a sequence of rounds
- substitutions and permutations conrolled by key
🟠 Data Encryption Standard(DES)
🔸 특징
- most widely used encryption scheme
- algorithm is referred to as the Data Encryption Agorithm(DEA)
- minor variation of the feistel network(kind of feistel)
🔸 Tripple DES
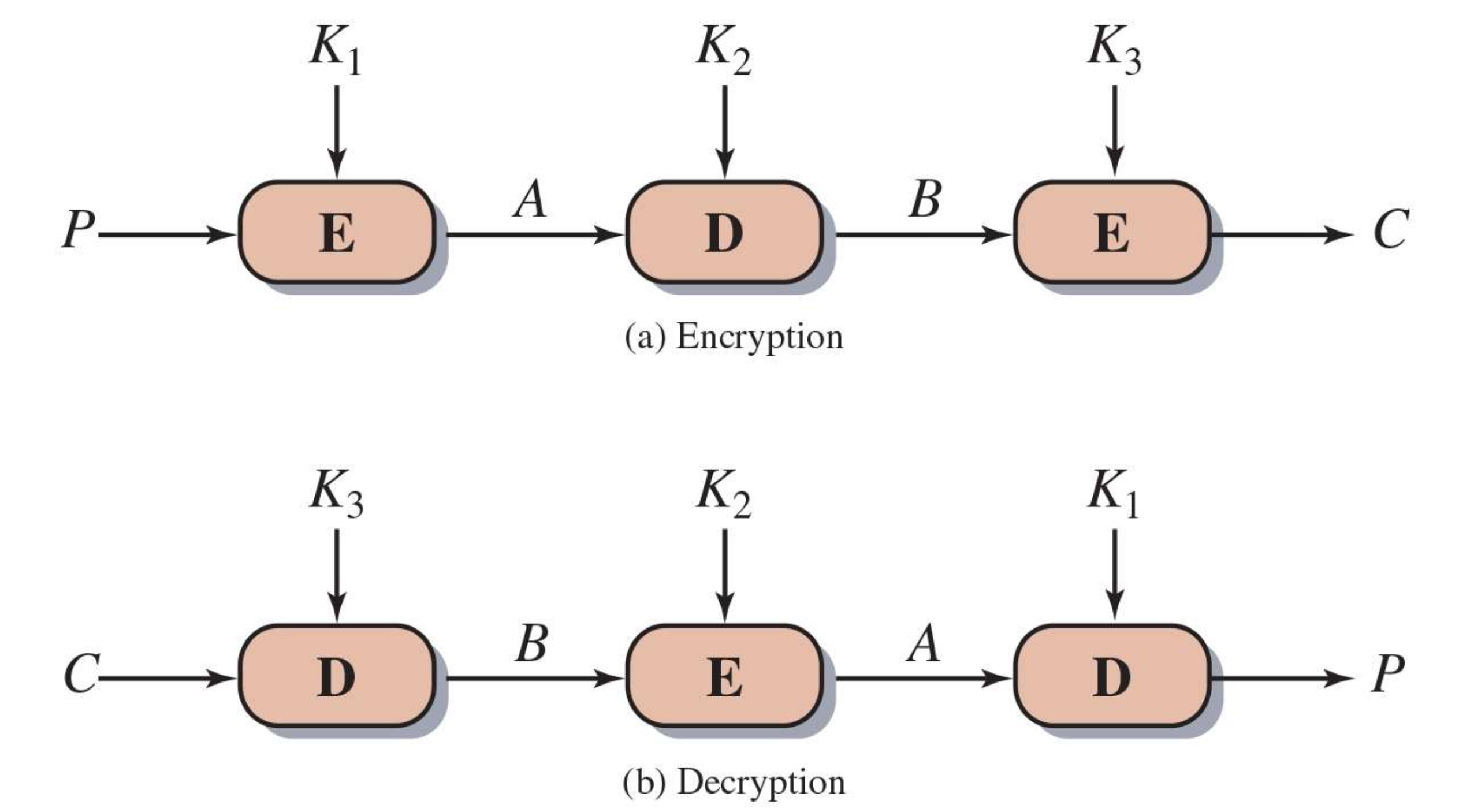
Why encryption 3 times?
- Triple DES (3DES) applies the DES encryption algorithm three times to enhance security because single DES (56-bit key) is vulnerable to brute-force attacks.
Why E-D-E, Not E-E-E?
- If the second DES operation (D) is replaced with an encryption (E), the scheme would not be compatible with standard DES.
- E-D-E allows compatibility with single DES by setting K1 = K2
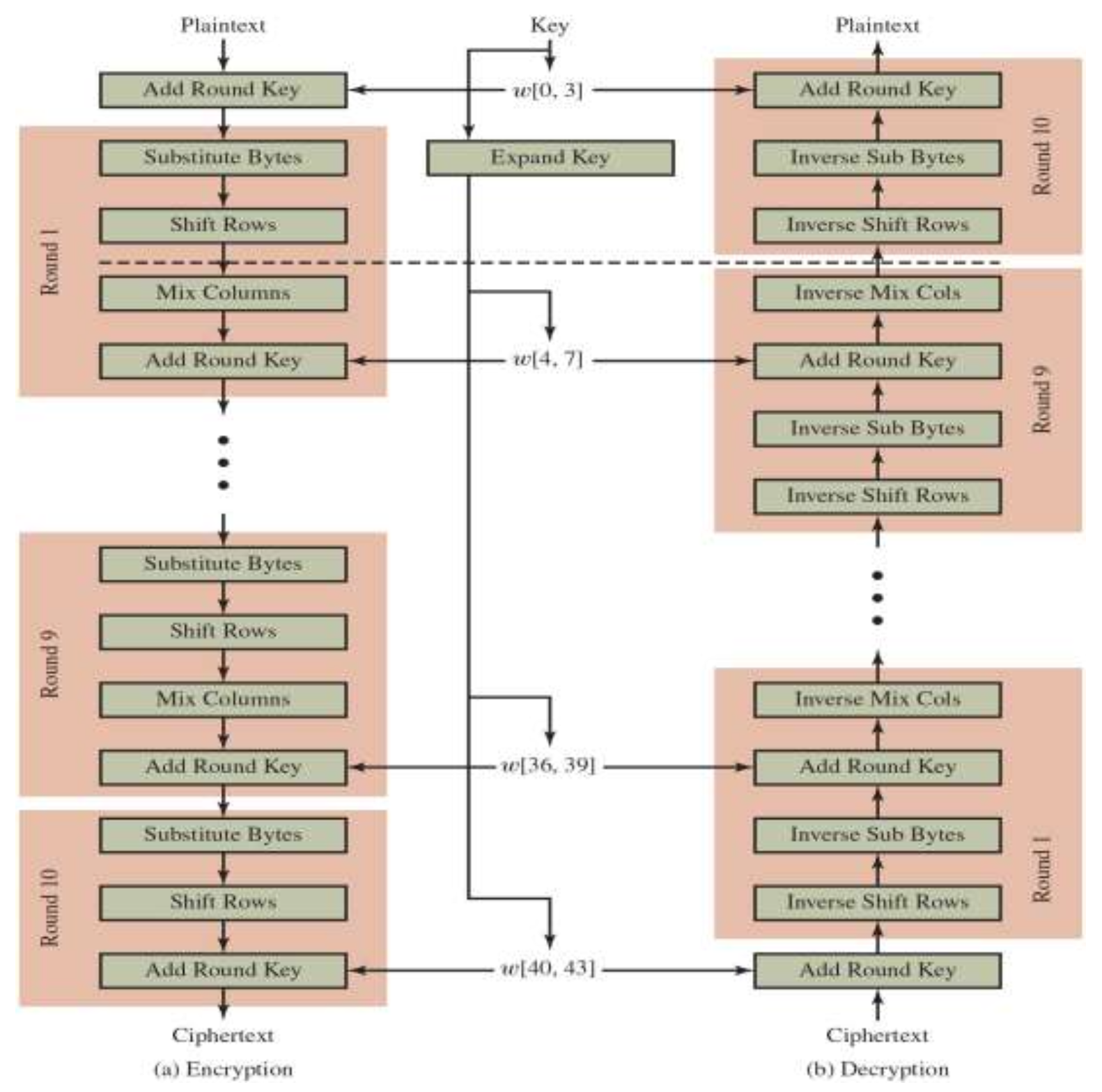
🟠 AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
- also block cipher. Not a stream cipher
🟠 Encryption of Frame Relay Network - End-to-End encryption vs Link encryption
🔸 Link Encryption
- requires to decrypt the packets when they arrive at a new router to figure out the next router that it will go to
- repeated encryption is costly if it performs encrypting payload part repeatedly
- However, key management cost is low
🔸 End-to-End Encryption
- no repeated encryption
- header cannot be encrypted otherwise intermediate routers cannot perform routing decision
- However, shared key need to be managed with every pairs(sender & receivers). So, high cost.
'Computer Science > 보안' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Information Security] Cryptographic Tools (0) | 2025.03.29 |
|---|---|
| [보안] CORS? (feat. SOP) (0) | 2024.04.29 |
| [보안] XSS와 CSRF의 개념과 비교 (0) | 2024.04.21 |




